
UPDATE 7 September 2012: NetApp has released its Virtual Storage Appliance, Data ONTAP Edge which is a licensed functional VSA.
One of the strengths of NetApp’s storage offering is that its controller operating system called Data ONTAP is the same across every NetApp Filer storage product they sell. This is hugely significant as it means if you know how to administer and configure the smallest FAS2000 Series Filers you are pretty much up to speed to administer and configure Filers up to their biggest and beefiest FAS6200 Series Filers so you don’t have to learn another management interface when you upgrade.
NetApp has also produced a Data ONTAP Simulator which in their words is a “A tool that gives you the experience of administering and using a NetApp storage system with all the features of Data ONTAP at your disposal.”
There have been various versions of the simulator over the years which initially could be installed on a simple RedHat or SuSE Linux box using emulated disks and have the same look and feel as a real NetApp Filer (without the rack space requirement or electricity bill!). Things progressed over the years and you could use more Linux distros. Nowadays there is a pre-built VMware virtual machine so you don’t have to install RedHat or SuSE beforehand.
Unfortunately the simulator is only available to existing NetApp Customers and Advantage Partners and requires a login to the NetApp Support Site, http://now.netapp.com
I was about to start a serious rant about this limited availability when surprisingly whilst writing this post Vaughn Stewart sent out a tweet that NetApp are in fact looking at the possibility of opening up access to the simulator for version 8.1 which is fantastic news.
I fiercely believe opening up access to learning and training tools allows so many more people to learn about your technology in their own time and if they know about your technology they are more likely to buy!
So, although the current status is the simulator is not available to all, hopefully this will change soon and this has saved me and you from a far longer rant!
There are however some limitations to the simulator:
- There isn’t any official support by NetApp and it works more on a community support model using NetApp’s community support forums.
- There is still quite a bit of configuration to do to get the simulator up and running, it’s not a plug and use VSA.
- The simulator is limited in the number of disks it can support and the size of the disks. In previous versions of the simulator it was provided with 2 x simulated shelves of 14 x 1 GB Disks with only 20 GB usable space which with some hacking could be extended by 2 more shelves. The current version 8.1 is provided with the same disk configuration but I’ll show you how this can be changed to use up to 4 x shelves of 4 GB disks with 180 GB available space which is a vast improvement and far more usable but you will need VMware Workstation to do this as ESXi doesn’t support changing the size of IDE disks.
- The simulator isn’t as robust as other true VSAs as it replicates a real Filer where you would have redundant PSUs so doesn’t play nicely when you just power it off! This is unfortunate as previous versions did seem to be a little more robust but the 8.1 version needs to be handled with care.
- You can’t by default connect to multiple simulators with NetApp OnCommand System Manager as the built in serial numbers are the same and System Manager doesn’t play nicely but I’ll show you how this can be changed.
- You can’t clone a fully configured simulator as you can’t change the serial number after the initial configuration.
- The simulator isn’t suited to running anything that is performance heavy as it is aimed at testing the software features rather than any IOPS benchmarking.
- Download the Simulator
- Add to VMware workstation or ESX(i)
- Increase the simulator VM disk size
- Amend the default serial number
- Run the initial configuration
- Add 2 new shelves of 14 GB Disks
- Move the current config to the new shelves
- Delete the 2 x shipped 1 GB disk shelves
- Add 2 x 4 GB Disk shelves to replace the shipped 1 GB disk shelves
Download the Simulator
The simulator can be downloaded from http://now.netapp.com/NOW/download/tools/simulator/ontap/8.0/ (you will need a NetApp login which is only available if you are a Customer or Advantage Partner)
Check that you can meet the hardware and software requirements listed on the download page.
I am going to set up and configure the 7-mode version rather than the cluster mode and on VMware workstation but you can upload the VM to ESX(i) but only after the disk size has been amended as you can’t amend an IDE disk in ESX(i).
Download the 7-mode version which is a .ZIP file either for VMware Workstation, VMware Player and VMware Fusion or the version for VMware ESX(i).
Add to VMware workstation or ESX(i)
Extract the .ZIP file. Copy the extracted files to a folder on your workstation or upload them to a datastore if you are going to be using it on ESX(i) but remember the issue with increased an IDE disk on ESX(i).
Double click on the .vmx file to add to VMware Workstation or browse the ESX(i) datastore and add to inventory.
You should now have a new VM called vsim-7m.
Rename the VM to what you will ultimately call your simulator to avoid confusion.
Edit the VM Settings.
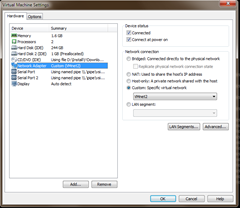
As this is a testing simulator for a virtual hosting environment I am going to only have 1 network card as I don’t need to test any network failover configuration but if you do need some more network functionality leave them in and configure them as you would a physical filer.
Set the Network Adapter to a Network connection or port group on your network.
Increase the simulator VM disk size
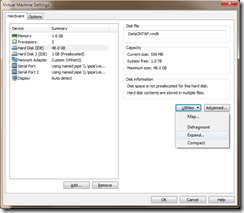
The shipped VM comes with a 48 GB VM disk which needs to be expanded to accommodate the new data in the emulated simulator disks when you write data to them.
You need to increase the VM disk size and then extend the partitions and also slices within the simulator to take advantage of the increased VM disk space.
The current 48 GB VM Disk contains 28 x emulated 1 GB disks and then has another 20 GB so if we are going to have 56 x emulated 4 GB disks + 20 GB then we will need a 244 GB VM Disk. I’m not sure if this is actually the correct figure but it works for me. You can make this VM disk thin-provisioned so you don’t have to have all 244 GB available until you write to it.
Edit the VM Settings and increase the HardDisk from 48 GB to 244 GB.
If you want to run the simulator on ESX(i) you can now upload it from VMware workstation with the amended IDE disk size.
The simulator VM runs on FreeBSD and uses the UFS file system. Unfortunately the usual Linux partition manager GParted can’t see UFS partitions so it isn’t much help so you need to use a FreeBSD boot disk.
I downloaded the FreeBSD 8.2 i386 LiveFS .ISO from freebsd.org.
ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/releases/i386/ISO-IMAGES/8.2/FreeBSD-8.2-RELEASE-i386-livefs.iso
Edit your simulator VM settings and add a new CD/DVD Drive as the simulator doesn’t come with one.
Attach the FreeBSD LiveFS .ISO
View the console so you can see the simulator boot process.
Boot the VM and change the BIOS boot order to boot first from CD-ROM.
Press Enter to Boot FreeBSD [default].
Select your country and press Enter.
Select your keyboard layout if prompted and press Enter.
Enter F and Enter to launch the Fixit repair mode option.
Select CDROM/DVD and press Enter.
You will now enter “fixit” mode.
Find the VM disk files:
1
| dmesg | grep VMware |
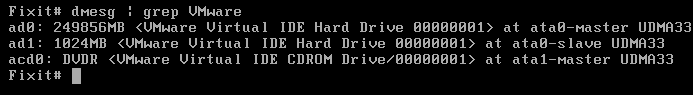
So, ad0 is the disk which is 244 GB.
To view the partitions on the disk:
1
| fdisk ad0 |
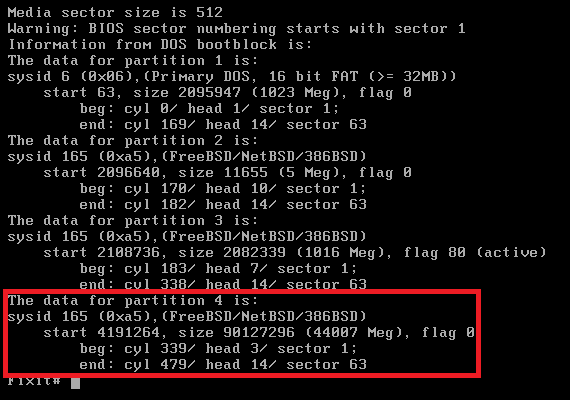
To extend the partition using the interactive slice editing process:
1
| fdisk –u ad0 |
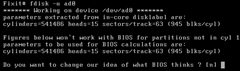
Press Enter to bypass editing the partitions until you get to partition 4 then type Y.
Press Enter to keep the default “sysid”.
Press Enter to keep the default “start”.
Now you need to enter the new sector size. I have worked out what the number needs to be in a completely non-scientific way using a whole host of different boot disks and a million different options! If someone else knows how to work this out in a far better way I would love to know how!
Enter 507513006 as the “size” and press Enter.
Press Enter to skip beg/end address.
You will now see a summary of the partition changes that fdisk will apply.
Press Y to be happy with the entry.
Press Enter to not change the active partition.
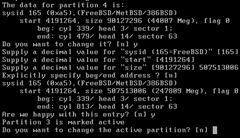
You will see a summary of the new partition table showing the new size of 247809 MB.
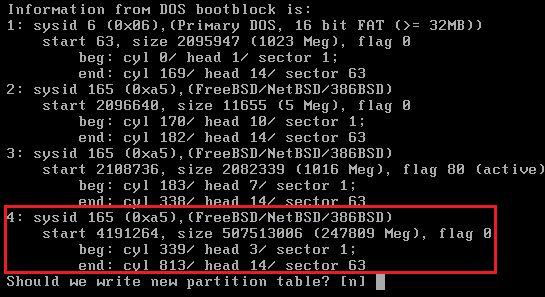
Press Y to write the new partition table.
You may get a message fdisk: Class not found but this can be ignored.
You then need to extend the slice in the partition.
To view the slices use:
1
| gpart list |
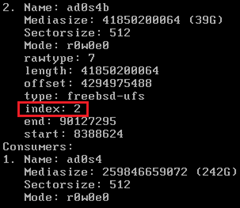
gpart by default will make the partition use all the available space. –i is the index number.
Extend the slice with the following command:
1
| gpart resize –i 2 ad0s4 |
The disk, partition and slice has now been extended and you can disconnect the mounted .ISO from the VM and shut down the simulator.
Amend the default serial number
Boot the simulator again.
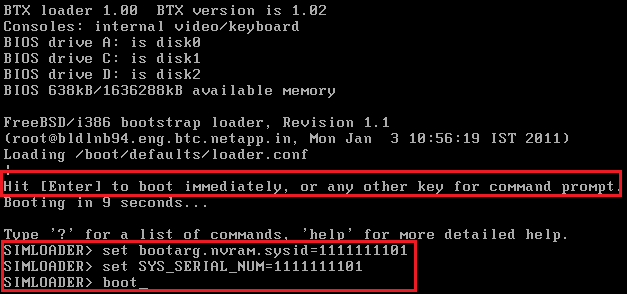
When you see Hit [Enter] to boot immediately, or any other key for command prompt, hit Ctrl-C.
You will then enter the SIMLOADER prompt.
I’ve used the same steps and number scheme from this NetApp Communities post.
Enter the following commands to set your unique serial number. (I’ve used 1111111101 – That’s 8 x 1s + 01)
1
2
3
| set bootarg.nvram.sysid=1111111101set SYS_SERIAL_NUM=1111111101boot |
Run the initial configuration
The simulator will continue to boot.
When you see Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu, hit Ctrl-C.
Enter option (4) Clean configuration and initialize all disks.
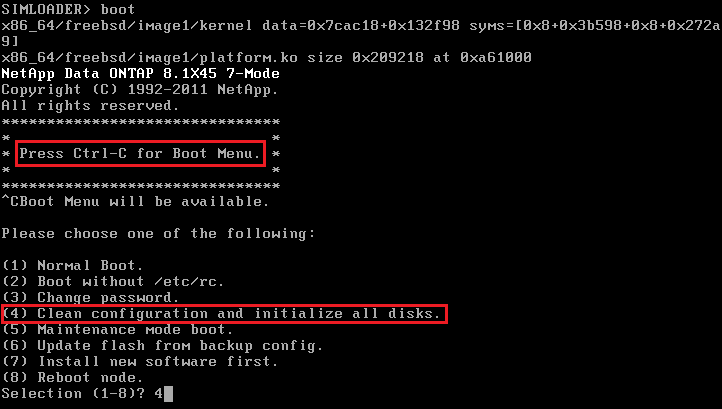
When the simulator says Zero disks, reset config and install a new file system, type Y.
Type Y to confirm erasing all the data on the disks.
The simulator will set up the disks and reboot.
Once it has rebooted the configuration will continue.
When prompted enter the new hostname. Mine is lonfiler01.
Press Enter to accept the default [n] for IPv6.
Press Enter to not configure interface groups.
Enter the IP address for your network.
Enter the Subnet Mask.
Press Enter to accept the default media type.
Press Enter to accept the default flow control.
Press Enter to accept the default of no jumbo frames.
Press Enter to not continue setup through the web interface.
Enter the default gateway IP Address.
Press Enter to bypass configuring an administrative host.
Enter a timezone.
Enter a location name.
Press Enter to accept the default HTTP root file directory.
Press Enter to not run the DNS resolver.
Press Enter to not run the NIS client.
Press Enter to continue, auto support will be turned off later.
Press Enter to not run the Shield Alternate Control Path Management interface for SAS shelves.
Enter and confirm the root password.
The initial configuration will continue. Once complete, press Enter to bring up a login prompt and enter the root password you had entered.
It’s now best to continue configuration through an SSH connection with Putty so you can copy and paste the configuration commands.
Some of the ONTAP functions are licensed already in the simulator but some aren’t so you may as well add all the options that aren’t added from this list.
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
| license add BSLRLTG #iscsilicense add BQOEAZL #nfslicense add ANLEAZL #flex_clonelicense add DFVXFJJ #snapmirrorlicense add DNDCBQH #snaprestorelicense add JQAACHD #snapvalidatorlicense add BCJEAZL #snapmanagerexchangelicense add RKBAFSN #smdominolicense add ZOJPPVM #snaplocklicense add PTZZESN #snaplock_enterpriselicense add PDXMQMI #sv_ontap_seclicense add RIQTKCL #syncmirror_local |
Now you are ready to add the new shelves.
Enter advanced mode and unlock the diagnostic user. Enter a password and confirm.
1
2
3
| priv set advanceduseradmin diaguser unlockuseradmin diaguser password |
1
| systemshell |
The next step will use the makedisks script to add 14 x 4 GB disks as shelf 2 and 3 of type 31 which is:
31 NETAPP__ VD-4000MB-FZ-520 4194,304,000 B 4289,192,960 B Yes 520
1
2
3
4
| setenv PATH "${PATH}:/sim/bin"cd /sim/devsudo makedisks.main -n 14 -t 31 -a 2sudo makedisks.main -n 14 -t 31 -a 3 |
Then exit the systemshell and lock the diaguser.
1
2
| exituseradmin diaguser lock |
1
| priv set admin |
1
| reboot |
Assign all the disks that are unowned to the filer.
1
| disk assign all |
We will move the current root volume vol0 to a new aggregate and new root volume on the new shelves.
First, create a new aggregate with the new shelves. Turn of checking for spare disks (which will still error in the logs but at least allow you to create a bigger aggregate) and set the raid group size to 28.
1
2
| options disk.maint_center.spares_check offaggr create aggr1 -r 28 28@4G |
1
| vol create vol1 aggr1 850m |
1
2
| ndmpd onndmpcopy /vol/vol0 /vol/vol1 |
Set the new volume as the root volume.
1
| vol options vol1 root |
1
| reboot |
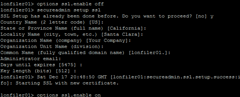
Something seems to go funny with the SSL certificates so you cannot also connect with OnCommand System Manager. The easiest way is to just recreate them.
1
2
| options ssl.enable offsecureadmin setup ssl |
Then turn back on SSL.
1
| options ssl.enable on |
Delete the 2 x shipped 1 GB disk shelves
Now we can remove the old vol0 and aggr0 as they are no longer holding the root volume.
1
2
| vol offline vol0vol destroy vol0 |
1
2
| aggr offline aggr0aggr destroy aggr0 |
Now we can remove the old disks and shelves.
1
2
3
| options disk.auto_assign offpriv set advanceddisk remove_ownership v5.* |
1
| disk remove_ownership v4.* |
We may as well rename the root volume and aggregate back to what they were originally just to keep things clearer.
Rename the existing root volume.
1
| vol rename vol1 vol0 |
1
| aggr rename aggr1 aggr0 |
Now we can go ahead and add 2 more 4 GB disk shelves to replace the 2 x 1 GB Disk shelves that have just been removed.
Enter advanced mode and unlock the diagnostic user. Enter a password and confirm.
Launch the systemshell and login as diag and enter the password you previously set.
1
2
| useradmin diaguser unlocksystemshell |
Now we need the remove the old simulated disks from shelf 0 and 1.
1
2
3
4
5
| setenv PATH "${PATH}:/sim/bin"cd /sim/dev/,diskssudo rm v0*sudo rm v1*sudo rm ,reservations |
31 NETAPP__ VD-4000MB-FZ-520 4194,304,000 B 4289,192,960 B Yes 520
1
2
3
| cd /sim/devsudo makedisks.main -n 14 -t 31 -a 0sudo makedisks.main -n 14 -t 31 -a 1 |
1
| exit |
1
2
| useradmin diaguser lockpriv set admin |
1
| reboot |
You may as well turn off the pesky autosupport warnings and then assign all the new disks that are unowned to the filer.
1
2
3
4
| options autosupport.support.enable offoptions autosupport.enable offoptions disk.auto_assign ondisk assign all |
1
| aggr add aggr0 28@4G |
You now have an aggregate spanning 4 x simulated shelves of 14 x 4 GB disks giving you 180.97 GB remaining available disk space after the root volume which is much better than the 20 GB you had initially!
Now is a good time to halt the filer and take a snapshot so you can easily revert if you have an issue.
You can also now go ahead and create your volumes and exports, LUNs, CIFS shares or whatever you want to use your simulator to test.
Remember, never just power off the simulator as you will land up with complicated wafl consistency issues which are difficult and sometimes impossible to fix.
Hopefully all these steps will be redundant when NetApp publicly release their simulator with the maximum possible disk size already configured and available as a simple to import virtual appliance.